Explore the exhibition







Traditional natural gas regenerative furnace with 6% electricity. 0.19 kg of emissions of CO2 per kg of glass.

Traditional natural gas
regenerative furnace with
6% electricity. 0.19 kg of
emissions of CO2 per kg
of glass.
Sustainable glass production: the furnace for the future
Sustainable glass production:
the furnace for the future
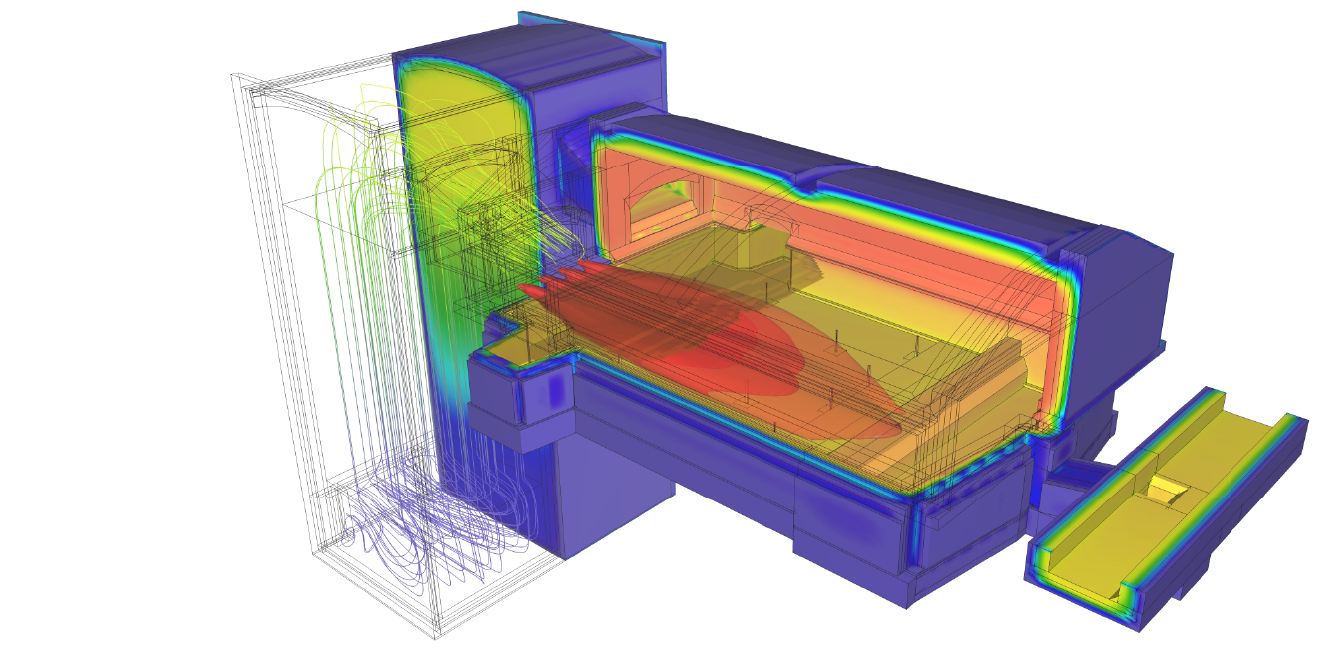
Melting glass requires considerable energy to reach the high temperatures required: over 1,500 degrees centigrade. This energy is generally obtained from fossil fuels, such as oil or natural gas, which produce the greenhouse gases responsible for global warming as they burn. However, the need to reduce the carbon footprint has rekindled interest in total or partial (hybrid) electric melting.
When this electricity comes from renewable sources, glass melting is essentially free of CO2 emissions and costs fall. In fact, even the smallest electric furnaces have thermal efficiency of between 70% and 85%, much higher than furnaces fuelled with fossil fuels. The glass melting furnaces of the future will use a higher percentage of clean renewable electric energy.

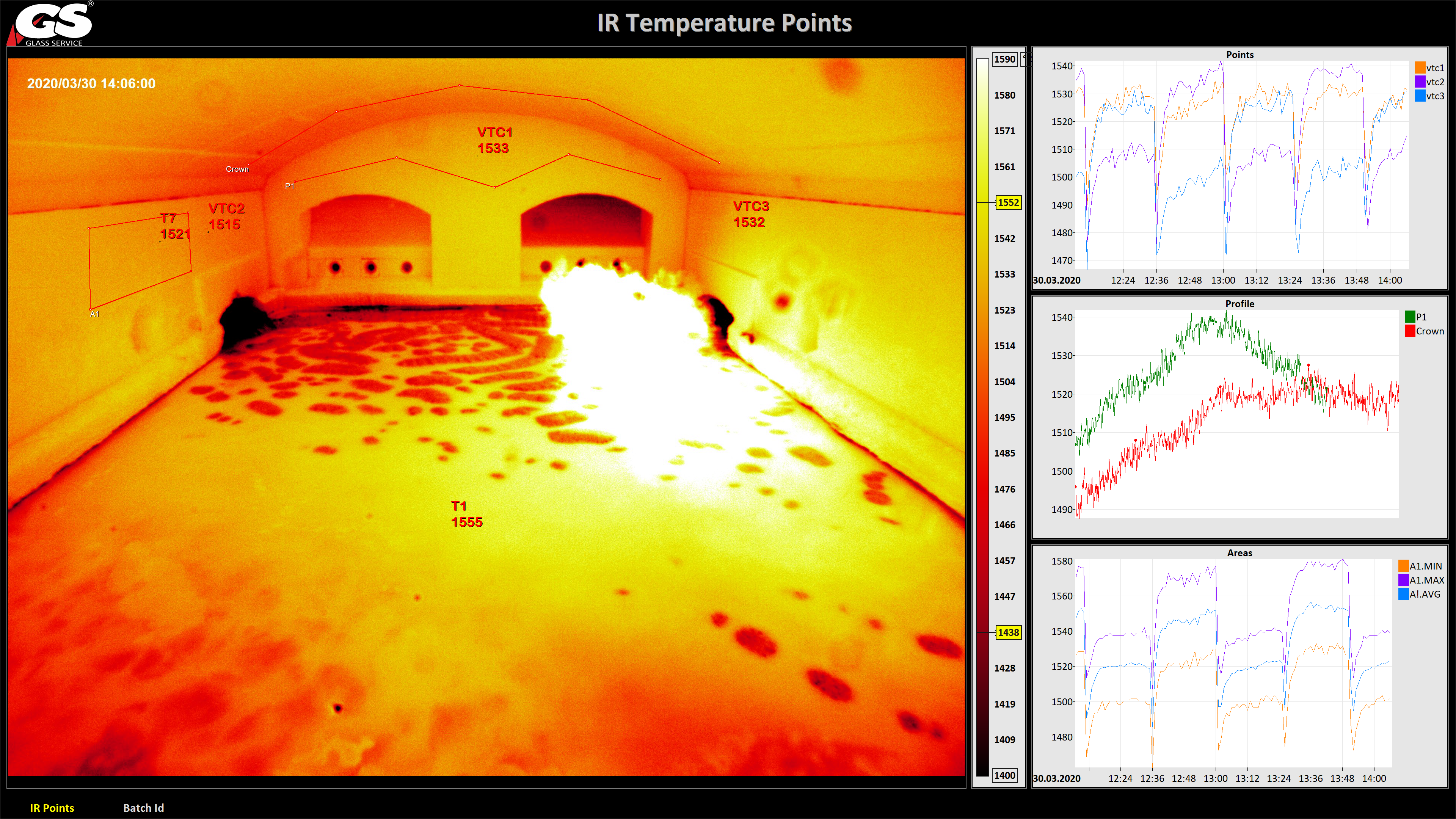
Smart furnaces
The endoscopic cameras of modern furnaces provide not only visual but also thermal information. When these cameras are equipped with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Neural Networks imaging technology, they are even able to recognize the behaviour of the fusion. With control software based on advanced models, this technology makes it possible to control the oven and the feeders 24 hours a day without operator intervention, which increases productivity while saving time and energy.
Melting glass requires considerable energy to reach the high temperatures required: over 1,500 degrees centigrade. This energy is generally obtained from fossil fuels, such as oil or natural gas, which produce the greenhouse gases responsible for global warming as they burn. However, the need to reduce the carbon footprint has rekindled interest in total or partial (hybrid) electric melting.
When this electricity comes from renewable sources, glass melting is essentially free of CO2 emissions and costs fall. In fact, even the smallest electric furnaces have thermal efficiency of between 70% and 85%, much higher than furnaces fuelled with fossil fuels. The glass melting furnaces of the future will use a higher percentage of clean renewable electric energy.

The furnace of the future will produce zero CO2 emissions as it will be fuelled with 80% renewable hydrogen and electricity.

Smart furnaces
The endoscopic cameras of modern furnaces provide not only visual but also thermal information. When these cameras are equipped with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Neural Networks imaging technology, they are even able to recognize the behaviour of the fusion. With control software based on advanced models, this technology makes it possible to control the oven and the feeders 24 hours a day without operator intervention, which increases productivity while saving time and energy.



