Explore the exhibition


Education in glass
Education in glass
Vitreous materials have played a fundamental role in education throughout history. For example, in the Middle Ages monks used glass lenses to continue to read and write until they were older, while alchemists developed glass laboratory equipment and material to study the medicinal uses of plants.
Today, many centres of education teach the practical aspects of glass art. As the courses focus on specific skills and techniques, some of them are short and allow amateurs to take part.
For their part, multinational glass companies promote training in-house or support education at colleges of education for apprentices and new technical staff. Specialist courses for more experienced staff, which are usually organized by commercial entities in the sector, do not only focus on skills acquisition but also on understanding and a profound analysis of processes.
1. The ICG organizes annual one-week summer and winter schools in France and China.
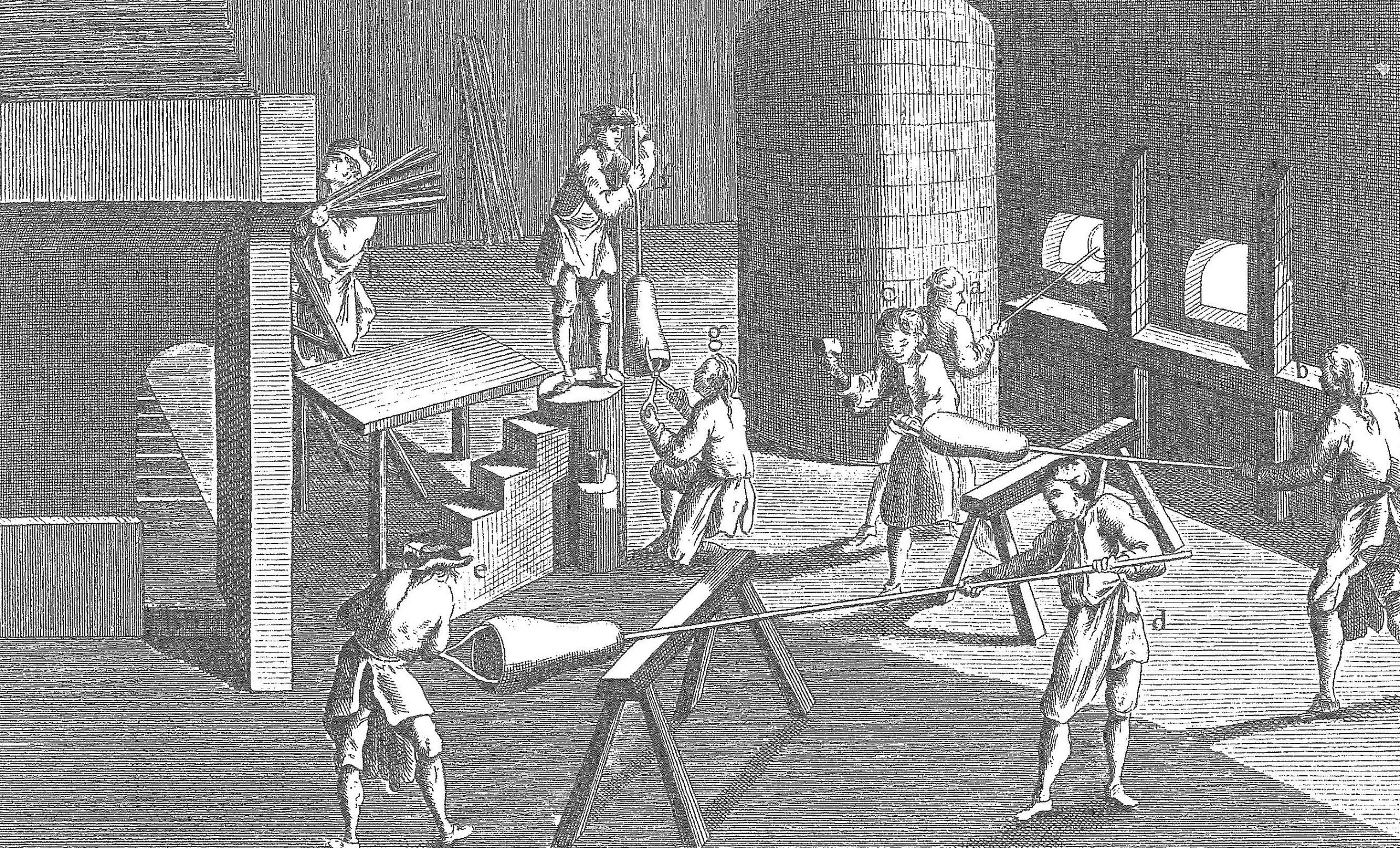
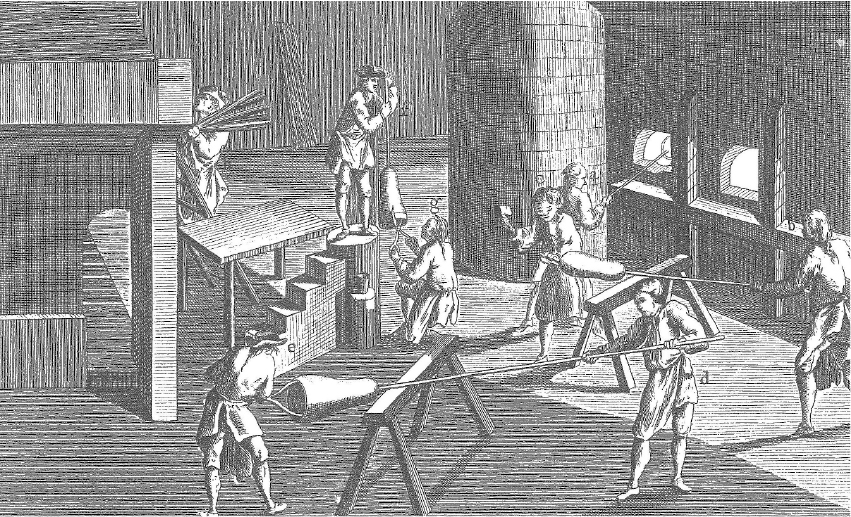
2. A picture is worth a thousand words. On many occasions, ancient historians used graphic images to illustrate manufacturing processes.
3. The ICG’s book Teaching Glass Better summarizes ten years of teaching experience.
4. In the past, the recipe books belonging to glass factory owners were closelyguarded secrets.
5. This drinking glass became the protagonist in a town whose economy depended on glass. It was made into the storyline of a great film when the worker who knew the secrets of its manufacture died. Education tries to note down, protect, transmit and analyse information.
In respect of academic institutions, a large number of universities offer courses on combustion, control, and civil and mechanical engineering but very few specialize in glass production. And this when the research of specialized departments often gives rise to a new generation of glass products and applications. International courses and conferences organized by institutions like the International Commission on Glass (ICG) play a complementary role in this process.
Vitreous materials have played a fundamental role in education throughout history. For example, in the Middle Ages monks used glass lenses to continue to read and write until they were older, while alchemists developed glass laboratory equipment and material to study the medicinal uses of plants.
Today, many centres of education teach the practical aspects of glass art. As the courses focus on specific skills and techniques, some of them are short and allow amateurs to take part.
For their part, multinational glass companies promote training in-house or support education at colleges of education for apprentices and new technical staff. Specialist courses for more experienced staff, which are usually organized by commercial entities in the sector, do not only focus on skills acquisition but also on understanding and a profound analysis of processes.
In respect of academic institutions, a large number of universities offer courses on combustion, control, and civil and mechanical engineering but very few specialize in glass production. And this when the research of specialized departments often gives rise to a new generation of glass products and applications. International courses and conferences organized by institutions like the International Commission on Glass (ICG) play a complementary role in this process.